What's the point of KPIs?

A business can drown in data - you need to know what to focus on. KPIs give you a reliable way of measuring your business performance quickly every month. This article looks at 6 KPIs for a retail or wholesale business selling physical products.
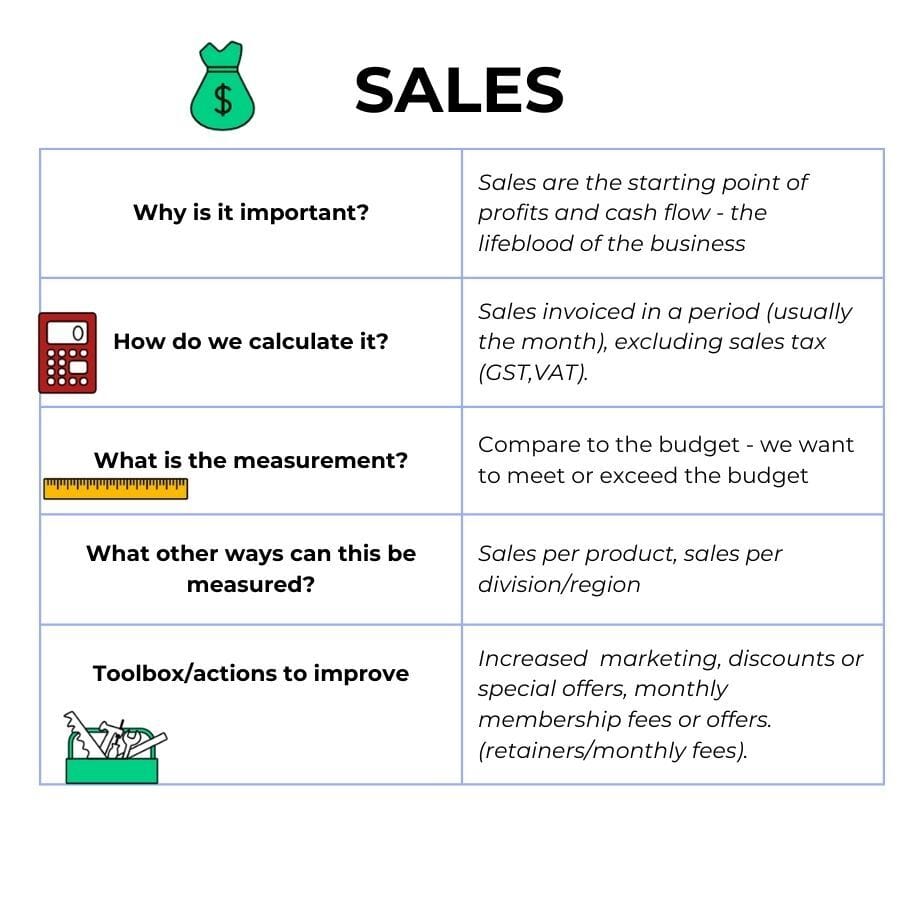
1.Sales
Sales are the starting point of profits and cash flow - the lifeblood of the business.
Sales should be measured in a way that makes sense for your business.
Branches or locations - measure sales per branch as well as overall
Product categories - divide your products into broad categories to track sales
Salesperson - measure sales per person to drive performance
Days or weeks - certain days may be more important than others in retail
Sales are measured excluding sales taxes collected (GST in Australia, VAT in Britain, South Africa).
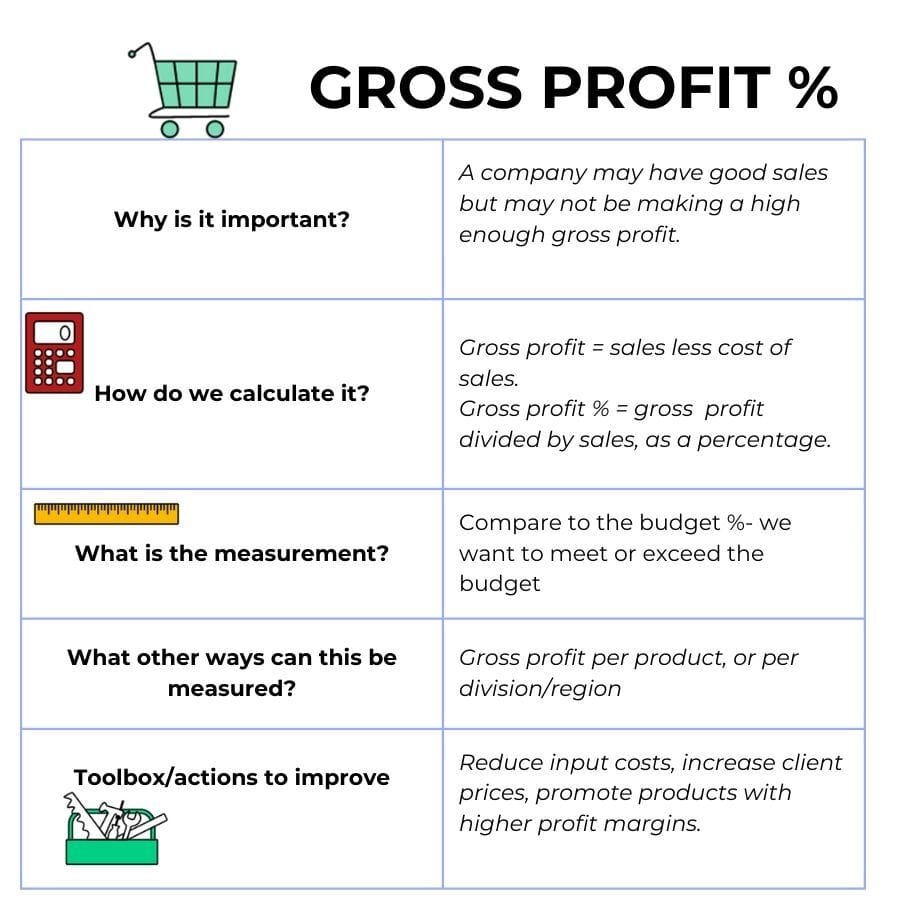
2.Gross profit
You may be achieving higher sales through discounts and lower prices, but that could mean lower profits. It's important to measure the gross profit percentage, not only the dollar value.
Costs creep up; your suppliers could increase costs and your margin will drop if you don't pass the increase on to the customer.
Gross profit should be measured in the same categories as sales - by division, product category and sales person. The gross profit on a certain product category may be higher or lower than the overall average, so it's important to look at gross profit in more detail.
3.Variable costs
Variable costs change from month to month and are often related to sales activities - advertising campaigns, sales bonuses or commission etc.
Why measure the percentage and not the dollar value? Because the increase in spend should lead to an increase in sales. Our aim could be to spend $1 and get $3 in sales - that is a ratio of 1/3 = 33% of sales.
An increase in dollar spend is not bad if we get the proportional increase in sales. If we are spending and not seeing the increase in sales, we aren't getting any bang for buck (or return on investment).
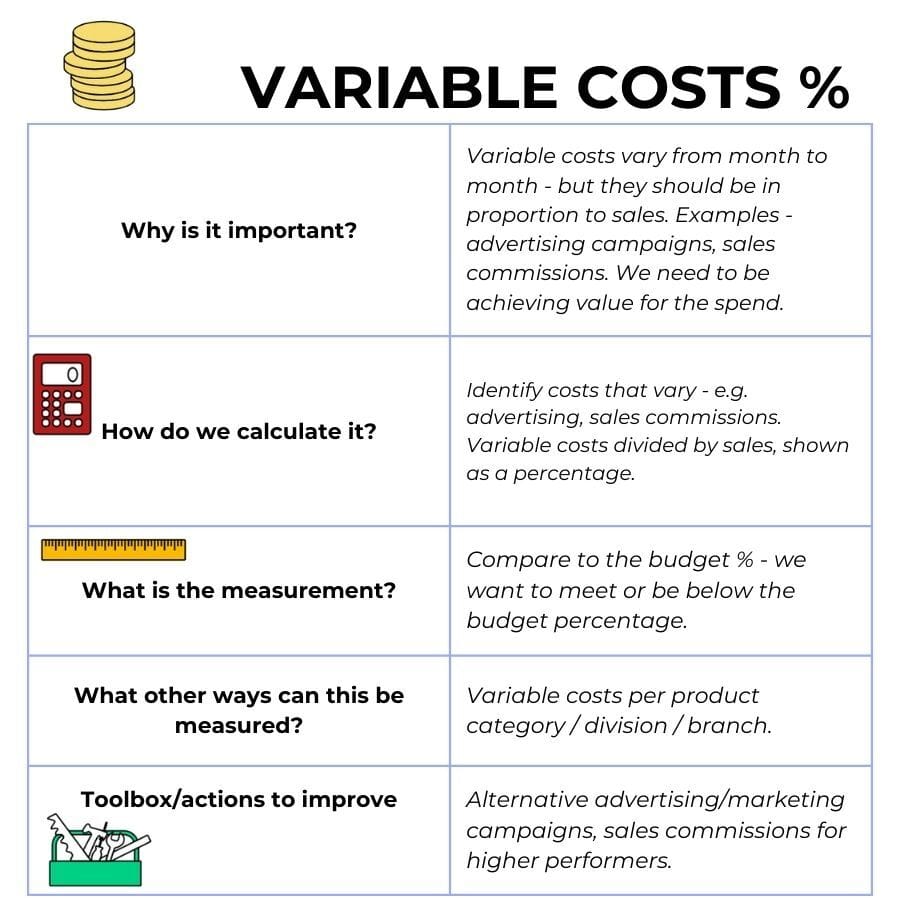
Table Head 1 | Table Head 2 | Table Head 3 |
|---|---|---|
Cell 1 | Cell 2 | Cell 3 |
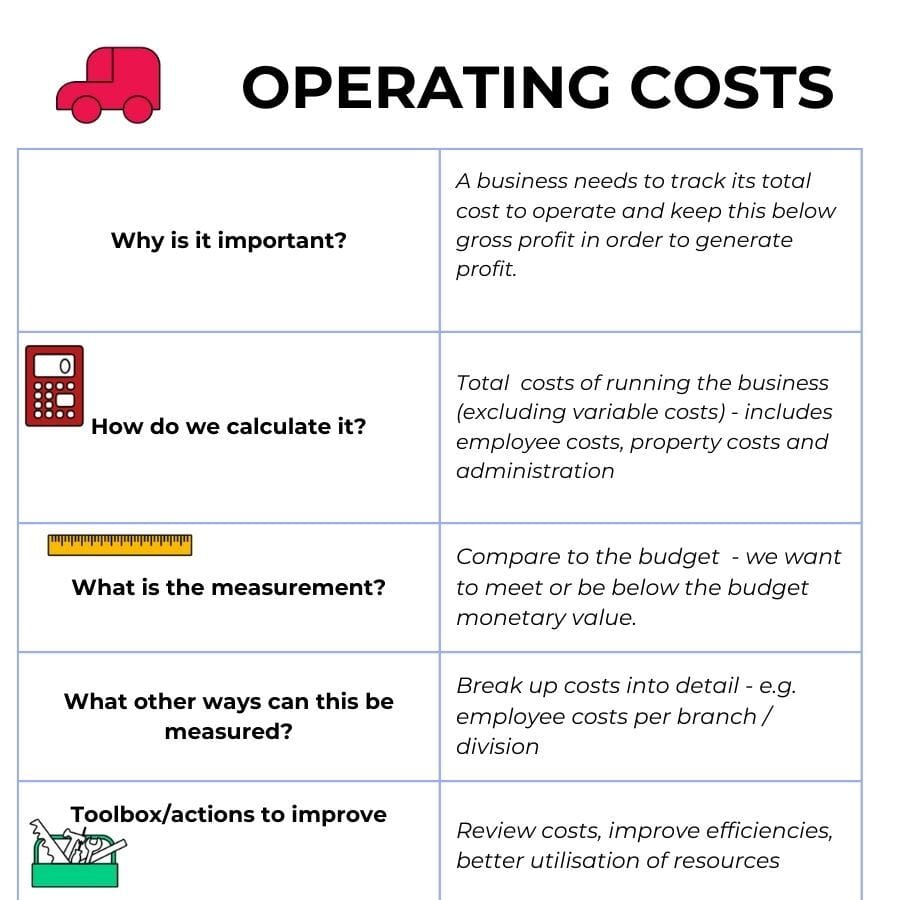
4.Fixed Operating Costs
Operating costs or running costs need to be controlled and kept below gross profit in order for the business to be profitable.
Costs should be analysed per division or branch to see that all areas are within budget.
5.Operating Profit
Ultimately, a business exists to be profitable. Operating profit is the most important measure of profitability - measure it in dollar value as well as percentage of sales.

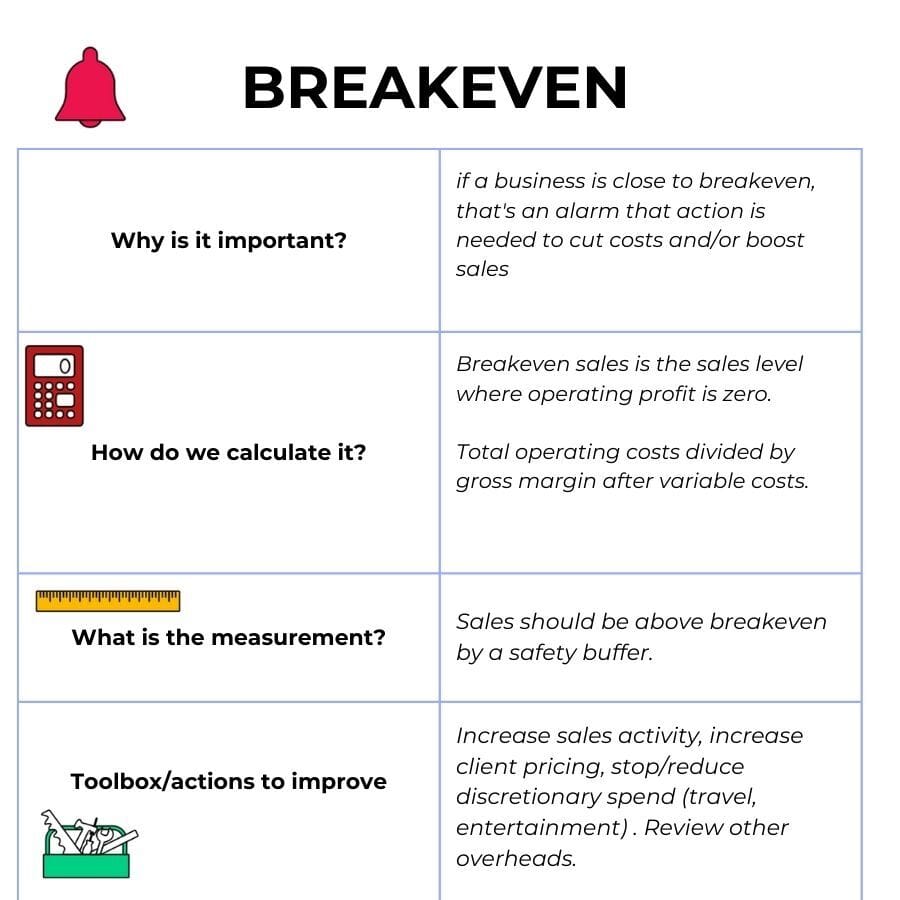
6. Breakeven
Breakeven means the sales level where profit = zero.
In other words, all costs are covered, but the business makes no money.
It's good to know that number - sales should be far above this to be safe.